Setup HTTPS Inspection
Overview
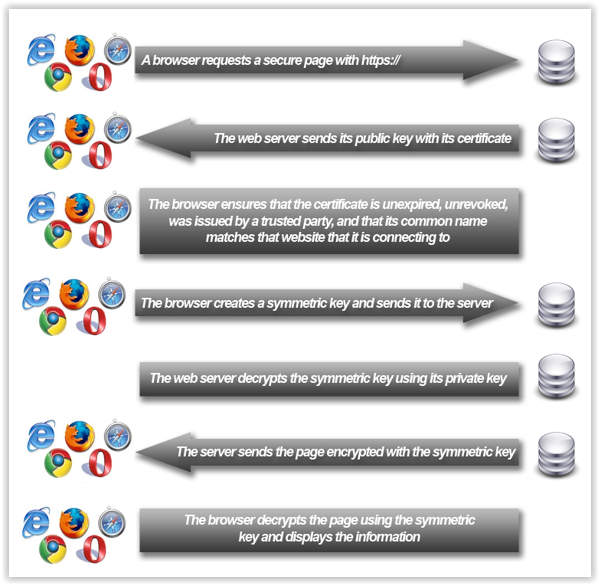
Over the past couple of years, the internet has changed its dimensions in terms of security. The web is shifting towards HTTPS, to deliver secure services to users. "The main motivation for HTTPS is authentication of the visited website and protection of the privacy and integrity of the exchanged data". The authentication happens based on the public key of the website verified by the client browser using trusted certificate authority. So, the users know, they are talking to the right websites and their data is safe.
Until 2010 only 20% of websites were using HTTPS protocol and the rest of 80% of websites were on HTTP. This equation started changing in 2010. For example, Earlier Google services including Google Search were running on HTTP, for security reasons Google started services on HTTPS over HTTP. This change in the web has thrown challenges to security vendors and customers, but both are ready for better web & security.
HTTP traffic is plain text-based message transfer over the network, the traffic can be seen and filtered by any device in the middle. Malware detection and data leak prevention are performed by security products on HTTP traffic to keep users and organizations safe. But HTTPS traffic is encrypted and traffic cannot be seen, or filtered without decrypting traffic and decryption is only possible by trusted parties.
Decrypting HTTPS traffic for scanning is called HTTPS Inspection. If security products do not scan HTTPS traffic, then some users can upload confidential documents to Google Drive and share to wherever they want. Also, such users can download a malicious file and spread it on the company network which can completely hit on organizational productivity. There are lots more that can happen, So Security experts always recommend the usage of HTTPS inspection-enabled products for enhanced security.
Most of the old security products implemented before 2010 cannot scan HTTPS traffic including SafeSquid NTLM editions. SafeSquid SWG was implemented in 2012 with HTTPS inspection support and continually improved HTTPS inspection performance with SSL context caching and session resumption techniques.
To perform HTTPS inspection, SafeSquid should have a trusted certificate authority (CA). You can use your enterprise CA as SafeSquid CA or You can generate a self-signed CA for an organization using SafeSquid's Self-Service Portal.
Client Scenario
The director of network security in a financial organization wants to protect the enterprise network from any external threats coming from the web in the form of malware. To accomplish this, the director appoints a Network administrator to make sure the computer network is up to date and operating as intended. The Network administrator needs to gain visibility into these sites otherwise bypass encrypted traffic and control access to malicious websites. The Network administrator should do the following:
- Intercept and examine all the traffic, including SSL/TLS (encrypted traffic), coming in and going out of the enterprise network.
- Bypass interception of requests to websites containing sensitive information, such as user financial information or emails.
- Block access to harmful URLs identified as serving harmful or adult content.
- Identify end users (employees) in the enterprise who are accessing malicious websites and block internet access for these users or block harmful URLs.
Solution
To achieve all the above, the Network administrator should set up a SafeSquid Secure Web Gateway (SWG) in the organization. The proxy server checks all the encrypted and unencrypted traffic passing through the enterprise network. It prompts for user authentication and associates the traffic with a user. URL categories can be specified to block access to Illegal/Harmful, Adult, Malware, and SPAM websites.
Benefits of HTTPS inspection
- Forbid the use of a personal Google account for any Google application like Gmail, YouTube, etc.
- Permit users with bypass privileges to access Facebook in Read Only mode. Users are not allowed to make posts, share, or play games, chat with other Facebook Users, post on their timelines, or Like posts made by others
- Enforce SafeSearch for users accessing Google Search, Yahoo Search, Bing Search, and YouTube.
- Permit use of Google SSO for login to web applications
- Use Virus scanning for both HTTP and HTTPS sites.
- Forbid users from uploading files to any website.
How does HTTPS work?
When you prepare your web server to use HTTPS you will be asked a few questions about your website and your company including your web site's domain name and your company's name and location. Your web server then creates two cryptographic keys: a private key and a public key. Your private key must remain private or the HTTPS connection could be made vulnerable. The public key does not need to be secret and is placed into a Certificate Signing Request or CSR, a piece of encrypted text that you will submit to a certificate authority. The certificate authority will validate your details and issue the SSL certificate which you can then install to the web server with the private key to enable HTTPS. For more information, see SSL For Newbs.
You can enable or disable HTTPS scanning from SafeSquid HTTPS inspection section.
How does HTTPS inspection work with SafeSquid?
- When user/client request a secure webpage say https://www.xyz.com (a HTTPS site) from the browser, SafeSquid will get CONNECT request from the client browser.
- SafeSquid will check configuration whether the user is allowed or denied to access to https://www.xyz.com. If access is denied to such websites, then, SafeSquid will send blocked template to that user's browser and closes connection.
- If access to https://www.xyz.com allowed to client then SafeSquid checks whether SSL inspection enabled for site or not?
If HTTPS inspection is disabled then SafeSquid resolve IP of xyz.com with the help of DNS and establishes connection to the www.xyz.com. Client browser checks the trust of the www.xyz.com server. Client browser encrypts data using server public key and sends back to server. There is no possibility for SafeSquid to check what client is sending to server and what is coming to client's browser from the server. SafeSquid will not check what is going on inside connection.
If HTTPS inspection enabled then
- SafeSquid resolves IP of www.xyz.com with the help of DNS and establishes connection to the www.xyz.com.
- SafeSquid performs SSL handshake with server.
- SafeSquid sends client hello message to the server in the process of SSL handshake.
- SafeSquid will get server public key in server hello message from the server in the process of SSL handshake.
- SafeSquid will check the trust of the www.xyz.com certificate with the help of trusted root ca bundle.
- If SafeSquid finds that certificate expired or invalid then SafeSquid allows or blocks the access to the site based on configuration.
- If SafeSquid finds that server certificate is valid then SafeSquid performs SSL handshake with client.
- After this SafeSquid uses server certificate (public key) to encrypt the data that will be sent to server. Further server can decrypt the data sent by the SafeSquid and returns response accordingly.
- SafeSquid performs SSL handshake with client Client browsers send client hello message to the SafeSquid server in the process of SSL handshake.
- SafeSquid will check whether public key and private key for www.xyz.com site does exist in the disk or not. If site does not exist then SafeSquid will create public key and private key for www.xyz.com and store them in the disk for reusability.
- SafeSquid will send back created server public key in server hello message to the client browsers in the process of SSL handshake with client.
- Client browsers further verify the trust of the certificate (public key) sent by SafeSquid. To verify the trusted certificate clients, need to import Safesquid.cer certificate into their browsers trusted authority. After this client uses SafeSquid created certificate (public key) to encrypt the data that will be sent to SafeSquid. SafeSquid can decrypt the data sent by clients with the help of created private key and checks the data and sends it to server by encrypting data with the server public key.
Configure the HTTPS inspection
Generate SSL (Self-Signed) certificates from self-service portal
You must generate an SSL certificate from the self-service portal before configuring HTTPS inspection.
Setup your SSL (Self Signed) certificates from self-service portal
When SafeSquid is installed in your network with HTTPS inspection enabled and the SSL certificate is not installed into the browser, then you will get an error while accessing the HTTPS websites. You must install the SafeSquid SSL certificate into the browsers.
Enabling HTTPS inspection on SafeSquid User Interface
Access the SafeSquid interface
Go to Configure Page
Open Real time content security side menu
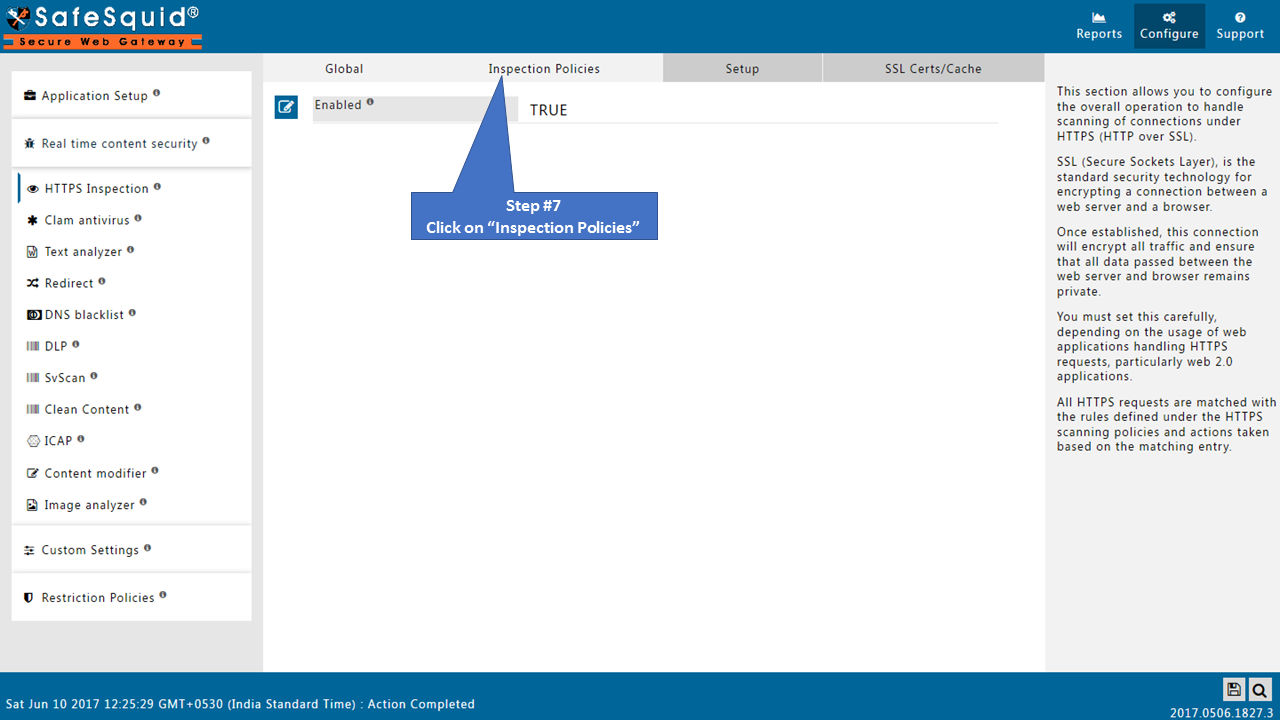
Open HTTPS Inspection section
Enable HTTPS Inspection
In newer versions of SafeSquid which are released after June-2017, setup tab is removed. You will see only three subsections in HTTPS inspection section.
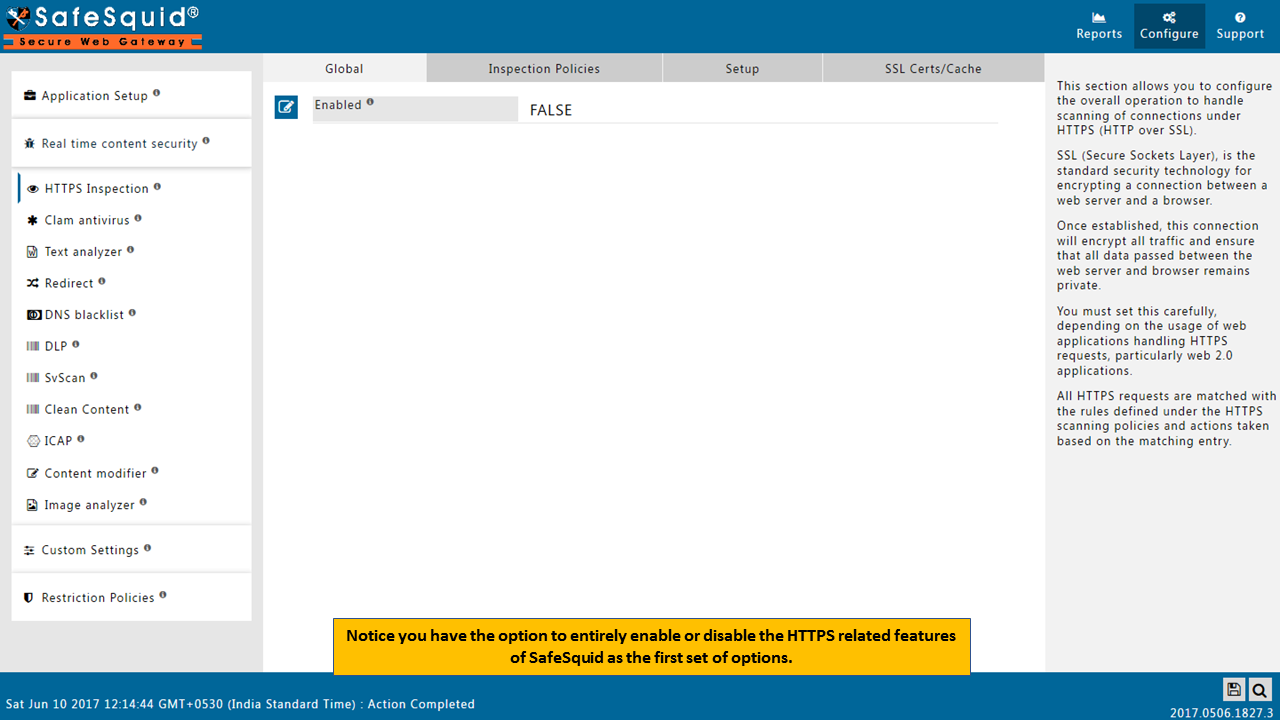
Open Global part of HTTPS Inspection section and make the Enabled as True.
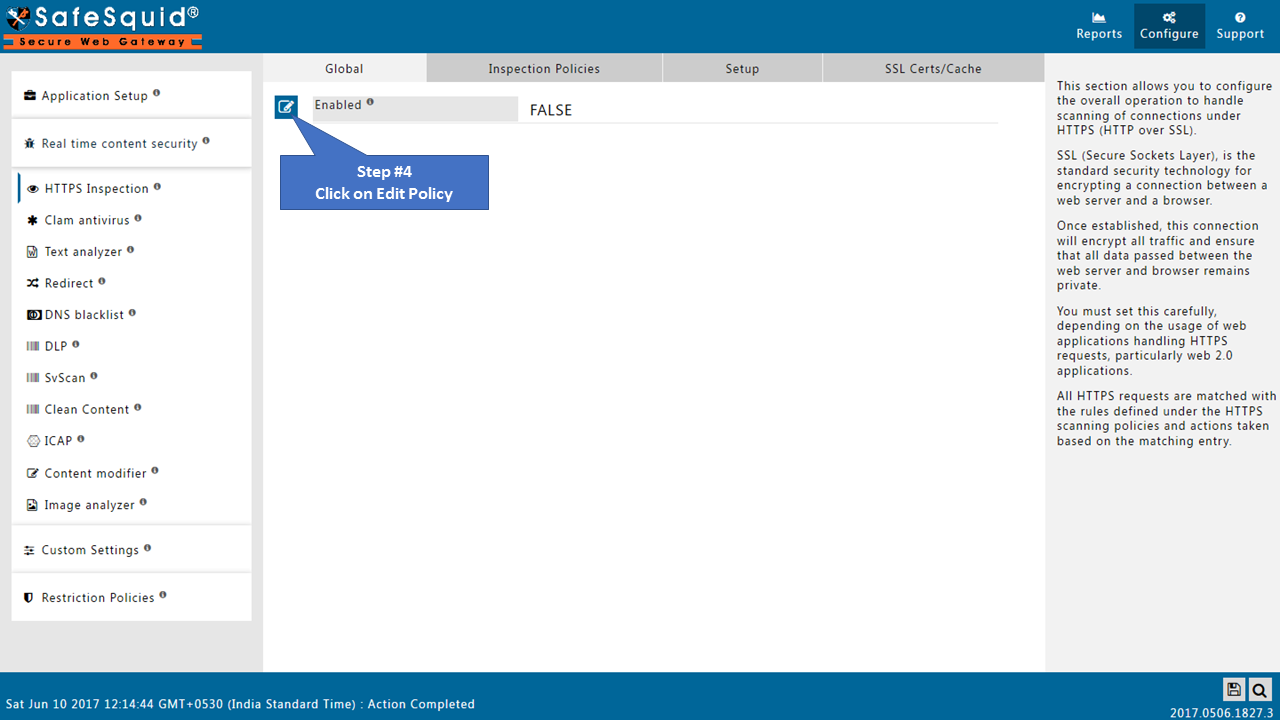
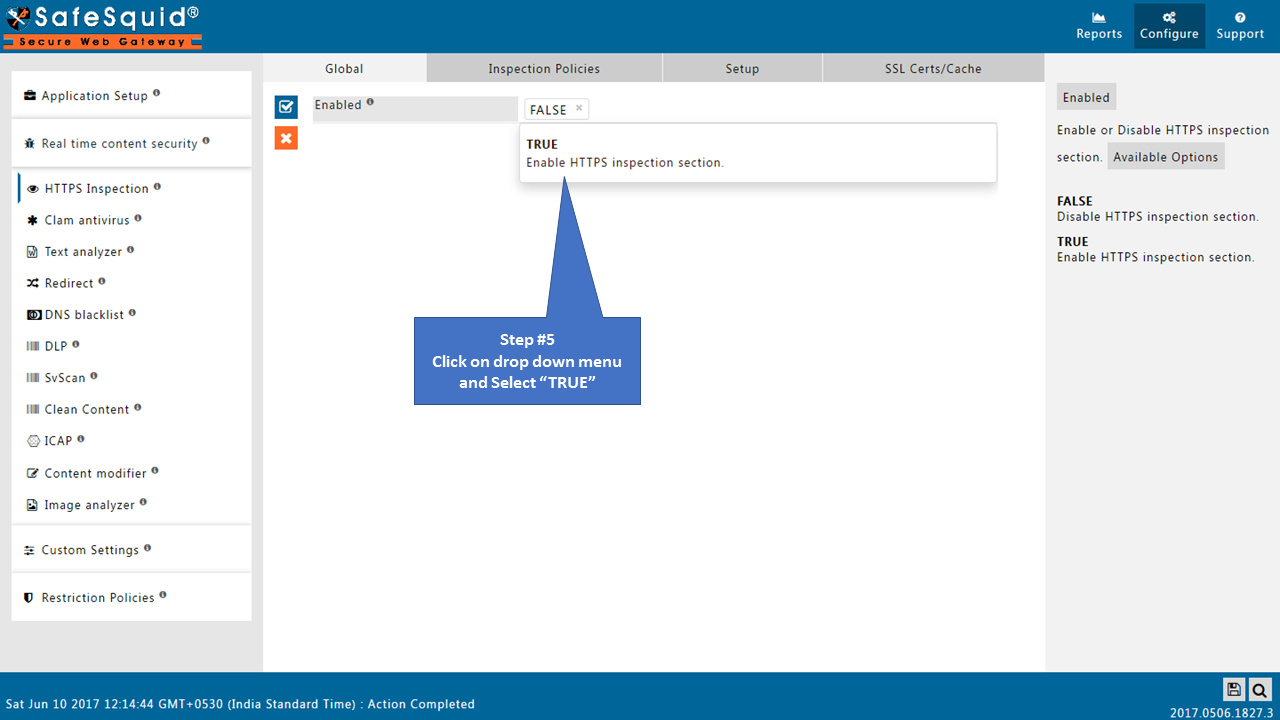
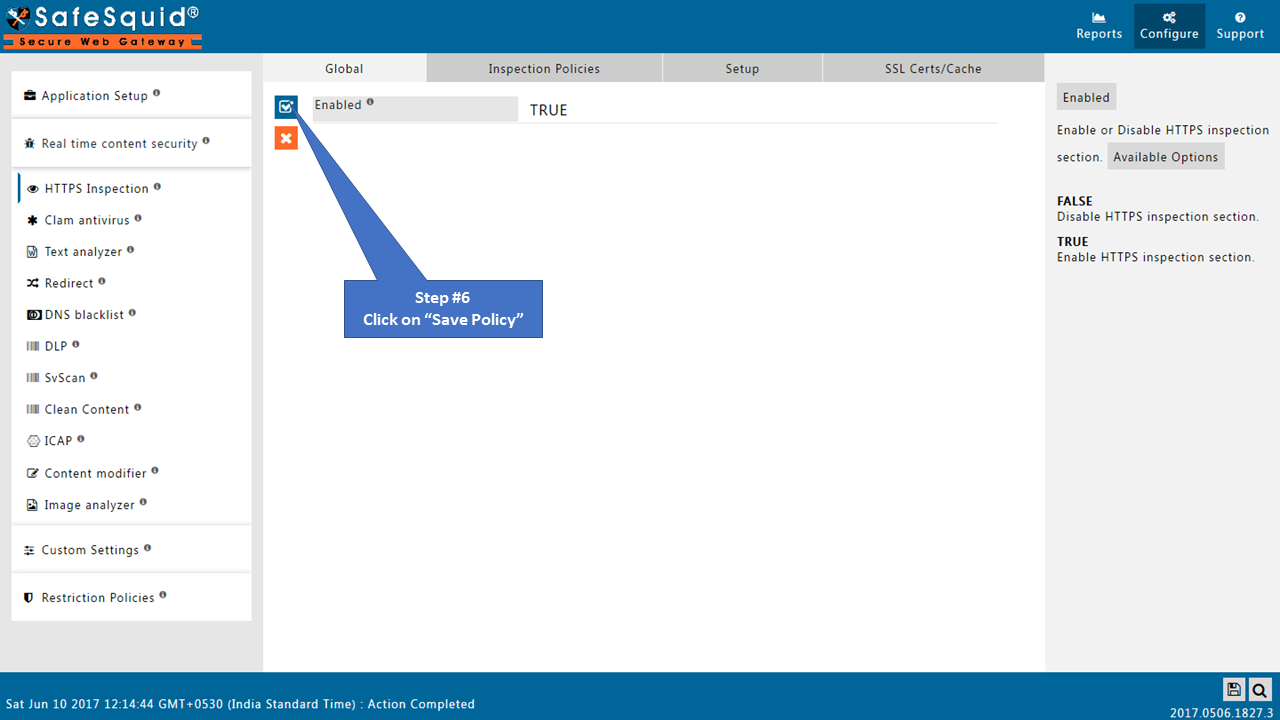
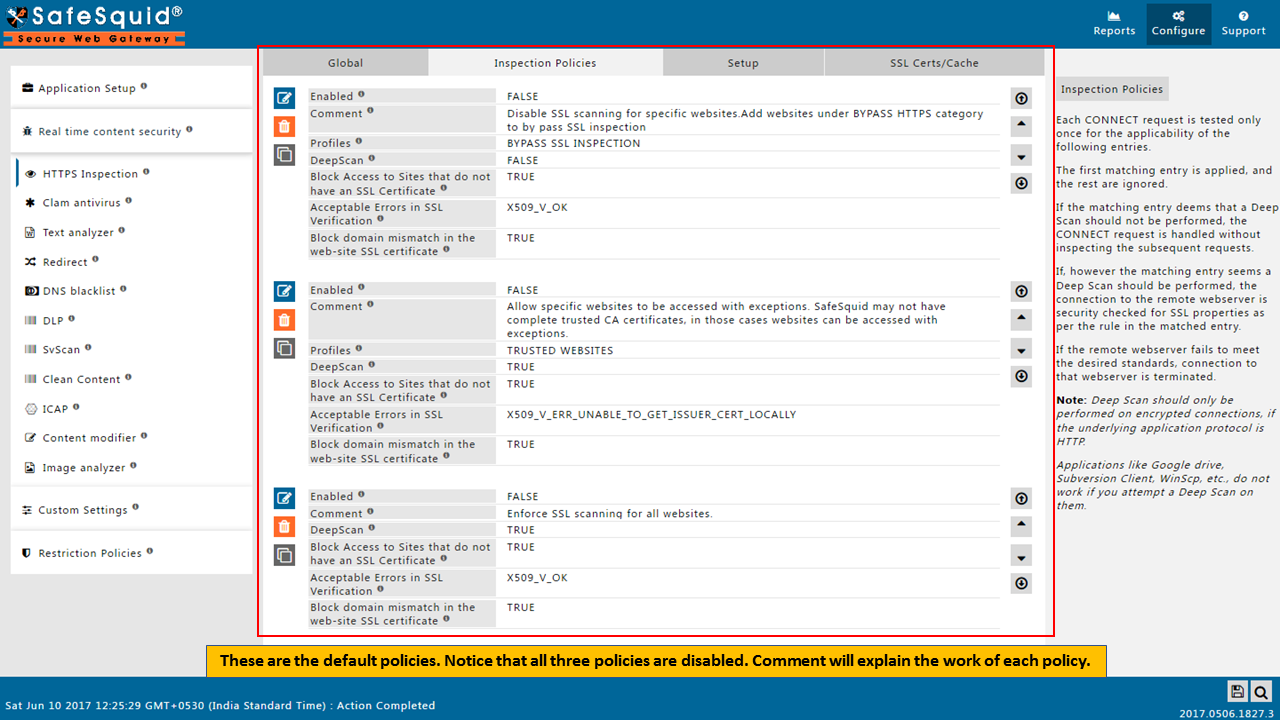
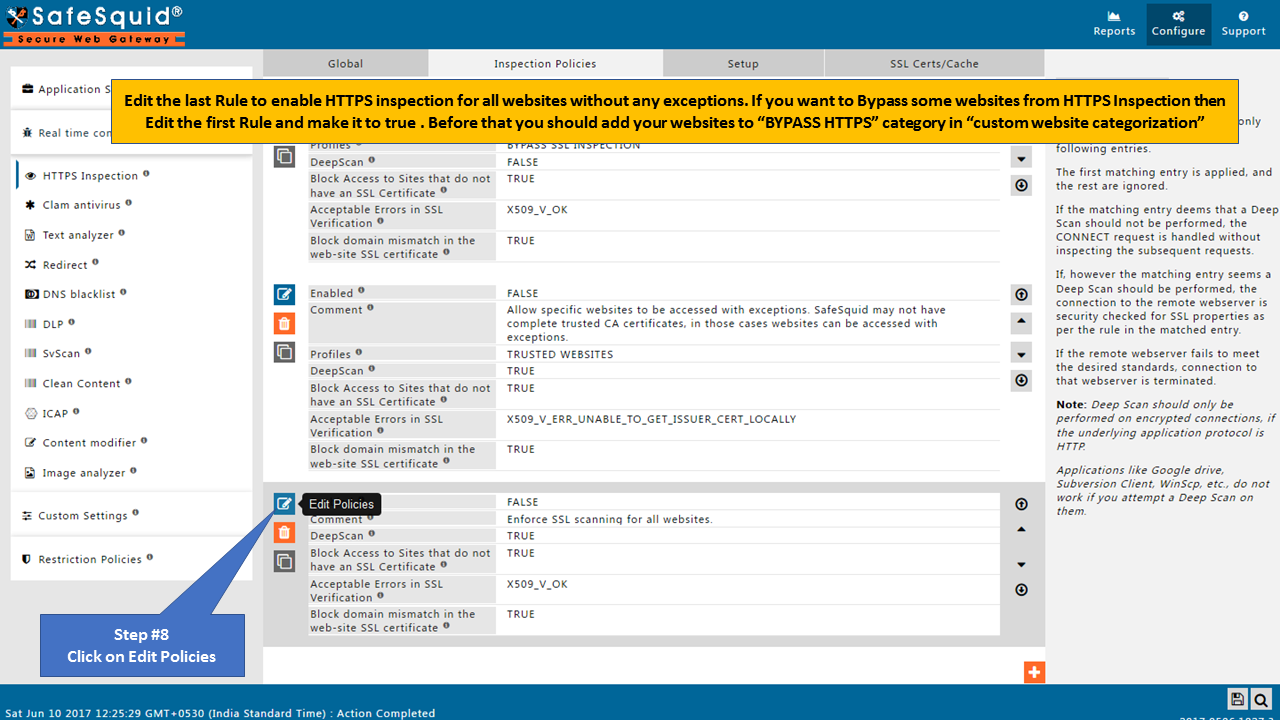
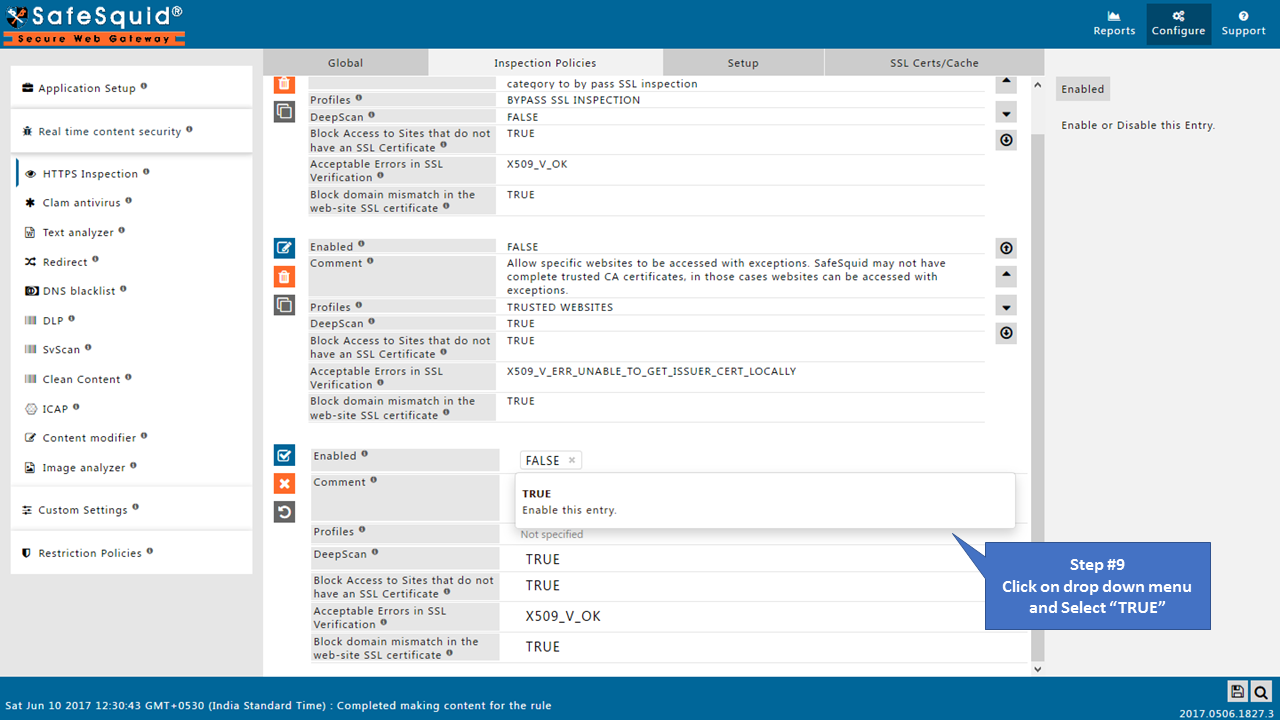
Open Inspection Policies Tab
Make sure all the policies should be Enabled as True.
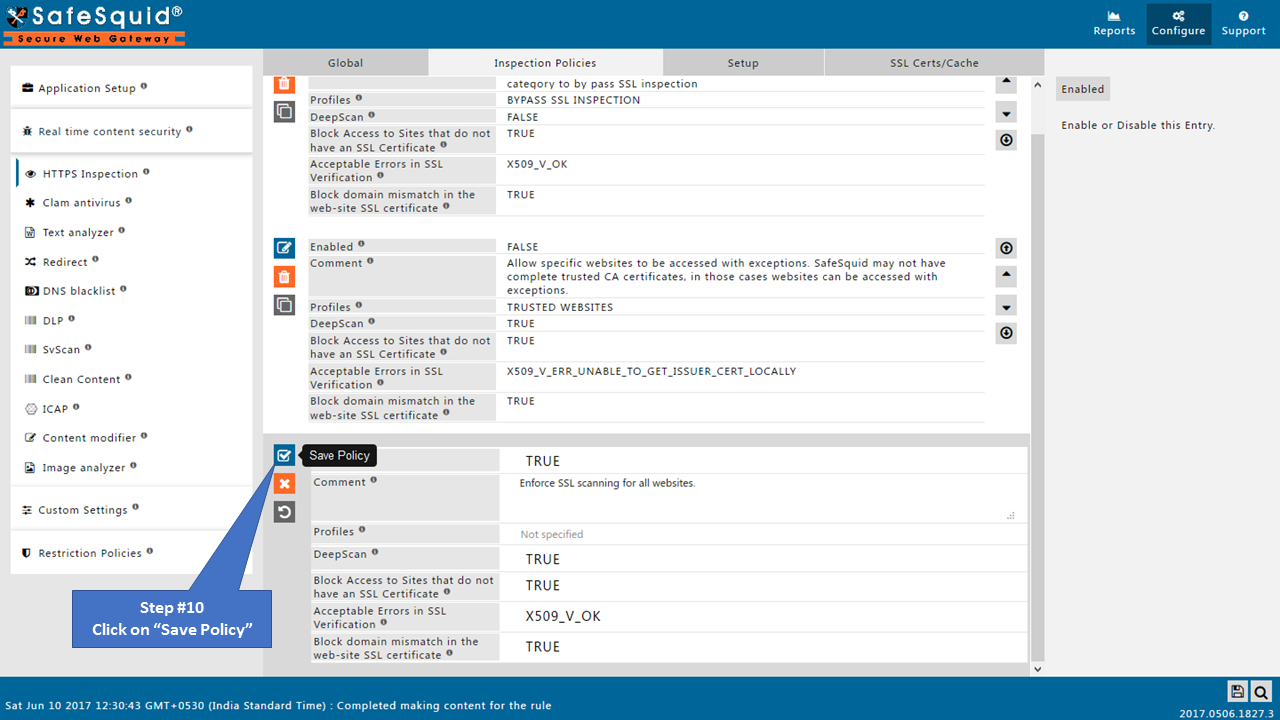
Save Configuration
Click on Save Configuration icon situated at bottom left corner.
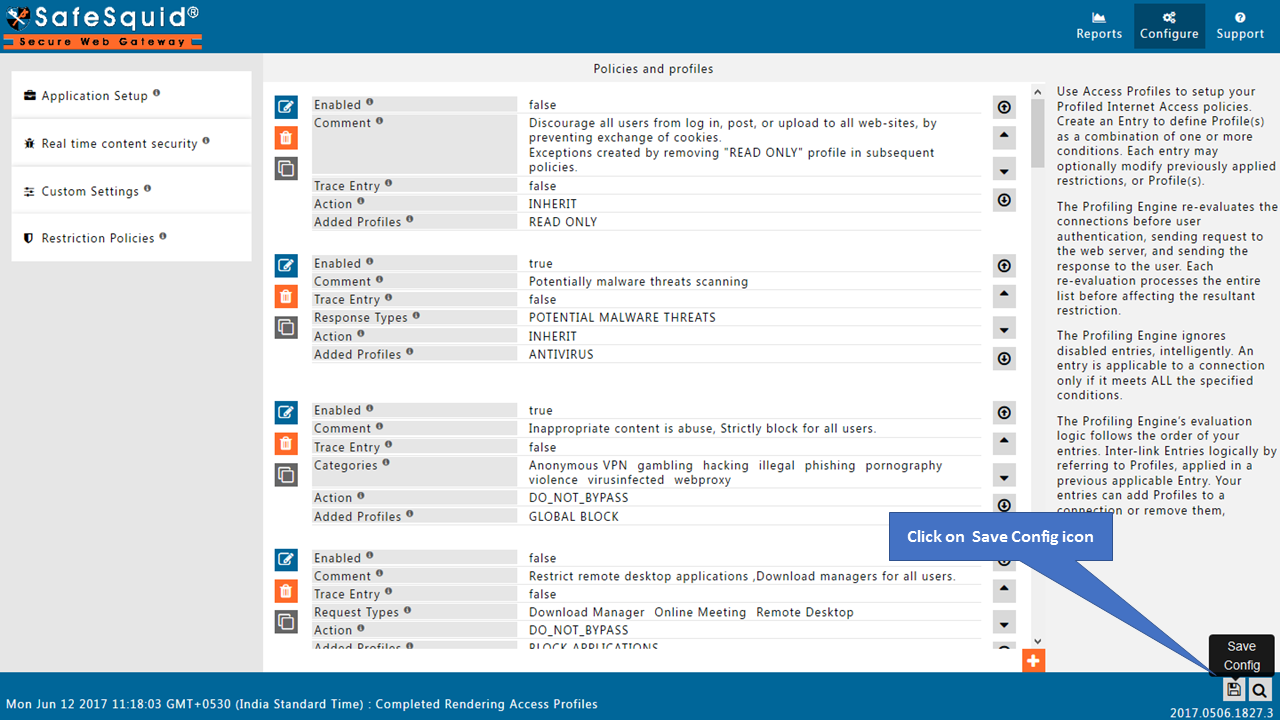
When you click on Save config, it will give a prompt for asking the confirmation to store your configuration into the cloud.
Select Yes only in below cases:
- if you want to use this same configuration in other SafeSquid instances.
- if your total configuration in all sections is completed and validated.
Otherwise select No and click on submit