Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)
Purpose
To provide a consistent and effective approach to troubleshooting network connectivity and web server issues using key commands.
Scope
This SOP applies to troubleshooting sessions involving DNS resolution, port connectivity, web server certificates, and web server responses, with and without proxy usage.
Procedure
Verify DNS Resolution
Use the command nslookup to check if the domain name can be resolved to an IP address.
nslookup hostname
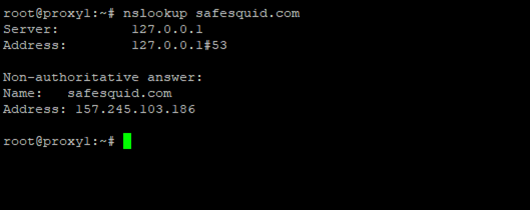
Successful scenario: Screenshot of successful nslookup output.
nslookup safesquid.com
Unsuccessful scenario: Screenshot of nslookup output indicating resolution failure.
nslookup safesquid.com
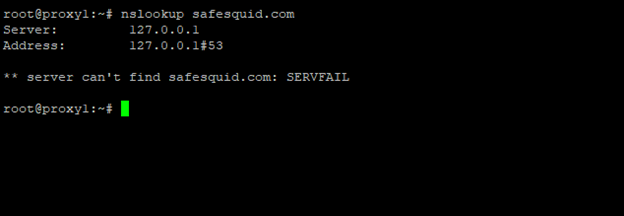 If the resolution fails, check DNS settings, server availability, and firewall rules.
If the resolution fails, check DNS settings, server availability, and firewall rules.
Check Port Connectivity
Use the command telnet to attempt a connection to port 443 on the server.
echo "" | telnet hostname 443
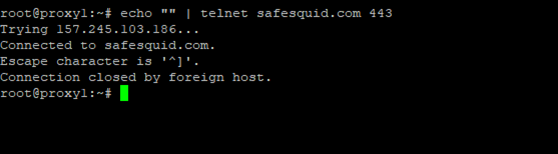
Successful scenario: Screenshot of successful telnet connection
echo "" | telnet safesquid.com 443
Unsuccessful scenario: Screenshot of telnet connection failure.
echo "" | telnet safesquid.com 443
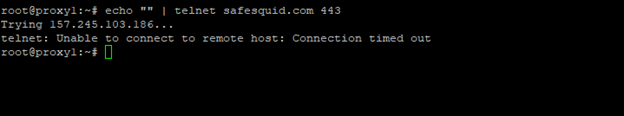
If unsuccessful, verify firewall rules, network restrictions, and server configuration.
Test Web Server Certificate (if required/ if the issue is related to server certificates):
Use the command openssl s_client to examine the server's certificate details.
echo "" | openssl s_client -brief -state -connect hostname:443 -verify_hostname hostname
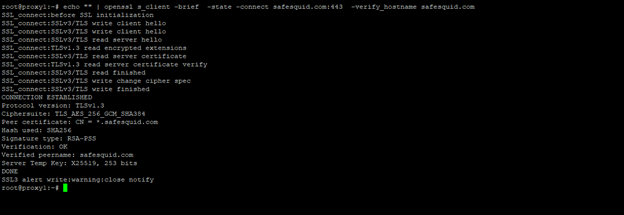
Successful scenario: Screenshot of valid certificate details from openssl s_client.
echo "" | openssl s_client -brief -state -connect safesquid.com:443 -verify_hostname safesquid.com
Unsuccessful scenario: Screenshot of invalid or expired certificate details.
echo "" | openssl s_client -brief -state -connect incomplete-chain.badssl.com:443 -verify_hostname incomplete-chain.badssl.com
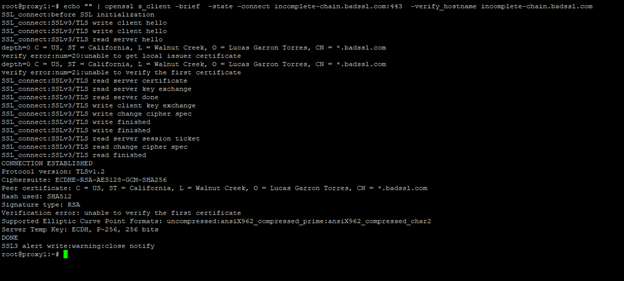
Check for validity, expiration, and compatibility with client requirements.
Check Web Server Response without proxy
Use the curl command to retrieve a response from the web server.
curl https://hostname --head
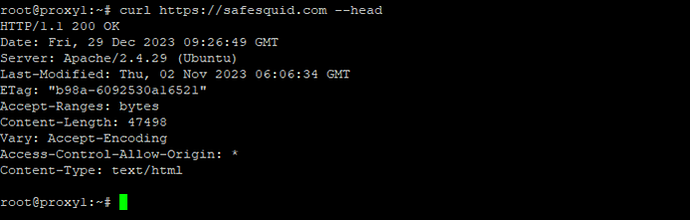
Successful scenario: Screenshot of successful curl output with a 200-status code.
curl https://safesquid.com --head
Unsuccessful scenario: Screenshot of curl output.
curl https://157.245.103.186 --head
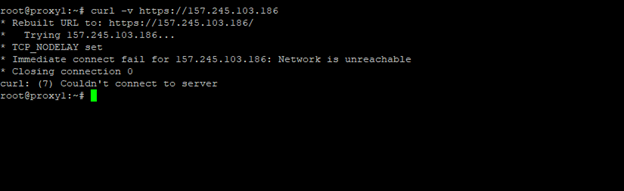
Analyze response codes (e.g., 200 for success, 404 for not found), headers, and content for troubleshooting purposes.
Check Web Server Response via Proxy:
Verify connectivity and web server response through the proxy.
Configure curl to use the proxy with the --proxy option to check the response via proxy.
curl --proxy 127.0.0.1:8080 --cacert /usr/local/safesquid/security/ssl/ROOT_X509File.cer https://hostname --head
Successful scenario: Screenshot of successful curl output with proxy enabled.
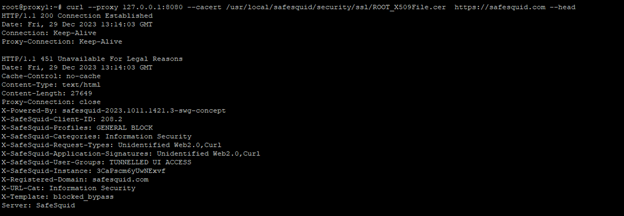
curl --proxy 127.0.0.1:8080 --cacert /usr/local/safesquid/security/ssl/ROOT_X509File.cer https://safesquid.com --head
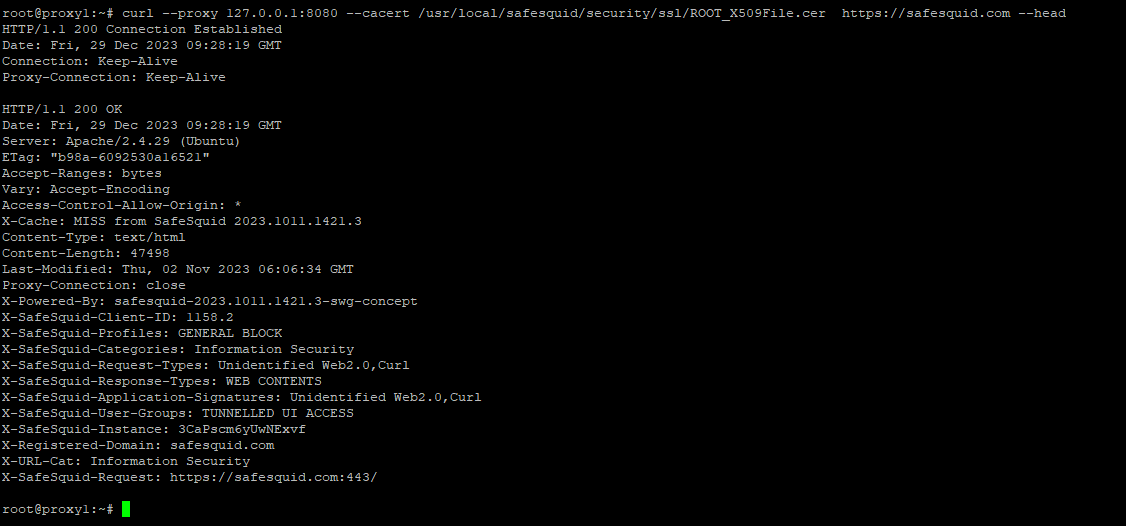
Unsuccessful scenario: Screenshot of curl output with proxy blocking.
curl --proxy 127.0.0.1:8080 --cacert /usr/local/safesquid/security/ssl/ROOT_X509File.cer https://safesquid.com --head
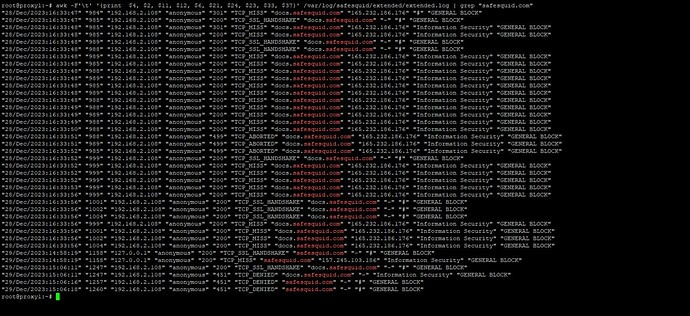
Access and Filter SafeSquid's Extended Logs:
Use the awk command to view a summary of connections related to the websites you are trying to debug for example "safesquid.com":
awk -F't' '{print $4, $2, $11, $12, $6, $21, $24, $23, $33, $37}' /var/log/safesquid/extended/extended.log | grep "website"
Example:
awk -F't' '{print $4, $2, $11, $12, $6, $21, $15, $24, $23, $33, $37}' /var/log/safesquid/extended/extended.log | grep "safesquid.com"
Customize the output with different log keys as needed.
Interpret the Output:
Each line represents a connection, providing key details:
Date and time
Client IP
Username
Status code
Referrer
Requested host.
Peer
Categories
Profiles
Check for status code which ranges from 400-500.
Requests which are blocked by SafeSquid will have a status code of 451.
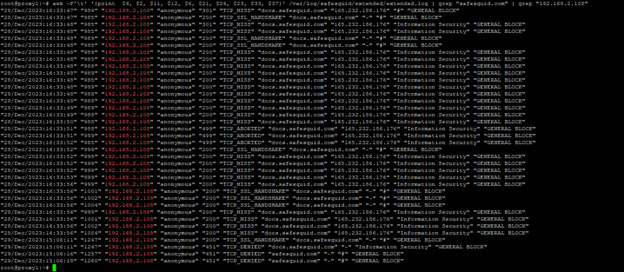
You can get more specific by mentioning IP or username to get user-specific logs.
awk -F't' '{print $4, $2, $11, $12, $6, $21, $24, $23, $33, $37}' /var/log/safesquid/extended/extended.log | grep "<WEBSITE>" | grep "<USER IP>"
Example:
awk -F't' '{print $4, $2, $11, $12, $6, $21, $24, $23, $33, $37}' /var/log/safesquid/extended/extended.log | grep "safesquid.com" | grep "192.168.2.108"
This will only show traffic to the proxy generated from the specified user to the specified website.
Available Log Keys:
- record_id
- client_id
- request_id
- date_time
- elapsed_time
- status
- size
- upload
- download
- bypassed
- client_ip
- username
- method
- url
- http_referer
- useragent
- mime
- filter_name
- filtering_reason
- interface
- cachecode
- peercode
- peer
- request_host
- request_tld
- referer_host
- referer_tld
- range
- time_profiles
- user_groups
- request_profiles
- application_signatures
- categories
- response_profiles
- upload_content_types
- download_content_types
- profiles
Look for status code of 400-500:
Focus on Connections with 400-500 status codes these often indicate blocks or errors.
Use find_client_id.sh for Detailed Logs:
Ensure that you have enabled debugging logs, you can find below how to enable debugging logs.
Logs are used to hunt issues and crashes and get a clear understanding of system behavior. Logs enable you to analyse issues with ease. SafeSquid provides such logs which are located at /var/log/safesquid/native/safesquid.log and /var/log/safesquid/extended/extended.log Respective logs while helping in your troubleshooting. By default, safesquid native logs do not provide comprehensive information. Using safeSquid's debug mode, the native log prints comprehensive details. Below is an example of ...
To retrieve complete logs for a specific connection, use find_client_id.sh script.
find_client_id.sh client_id | less
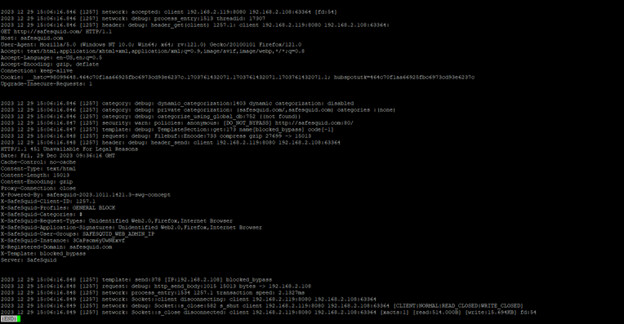
Check for any errors in the given connection.
Consult SafeSquid Support (If Necessary)
If you are unable to resolve the issue after following the troubleshooting steps, contact SafeSquid support for further assistance.
Before contacting support, create a text file containing the detailed logs for a specific connection using the following command:
find_client_id.sh client_id > /home/administrator/error_client_id.txt
Replace client_id with the actual client ID.
Example:
find_client_id.sh 1257 > /home/administrator/error_1257.txt
Attach this text file to your support ticket to provide the technicians with comprehensive information for better troubleshooting.
Unable to find the root cause of your problem.
After trying all the mentioned troubleshooting steps, if you are still not able to figure out and solve your problem then consult SafeSquid's support specialist with the output of your find_client_id.sh attached in your email.
To save the output of find_client_id.sh, redirect the output to a text file as shown below.
find_client_id.sh 1257 > /home/administrator/error_1257.txt
When sending a support ticket for your issue add the file error1257.txt for the support technician to support you better.
Troubleshooting Tips
- Identify Blocks: Look for blocking messages in the logs.
- Status code 451 indicates that the website is getting blocked due to proxy rule.
- Check Configurations: Review proxy rules and settings for potential misconfigurations.
- Analyze Detailed Logs: Use find_client_id.sh to pinpoint specific issues.
- Seek Further Assistance: If you need more help, consult SafeSquid documentation or contact their support team.
Remember
- Always enable debugging mode before troubleshooting.
- Adapt the commands and log keys to your specific needs.
- Consult SafeSquid documentation for more advanced troubleshooting.
If you are unable to identify the problem, share the output of find_client_id.sh with SafeSquid's Support team at support@safesquid.net